Solid Liquid Separation Systems
Systems

GMM Pfaudler has consistently been recognized as a premier provider of advanced technology and solutions spanning multiple industries for over seventy years. The offerings of GMM Pfaudler now includes continuous processing equipment and systems for Solid Liquid Separation (SLS) that leverage Hindustan Dorr Oliver Technology (HDOT).
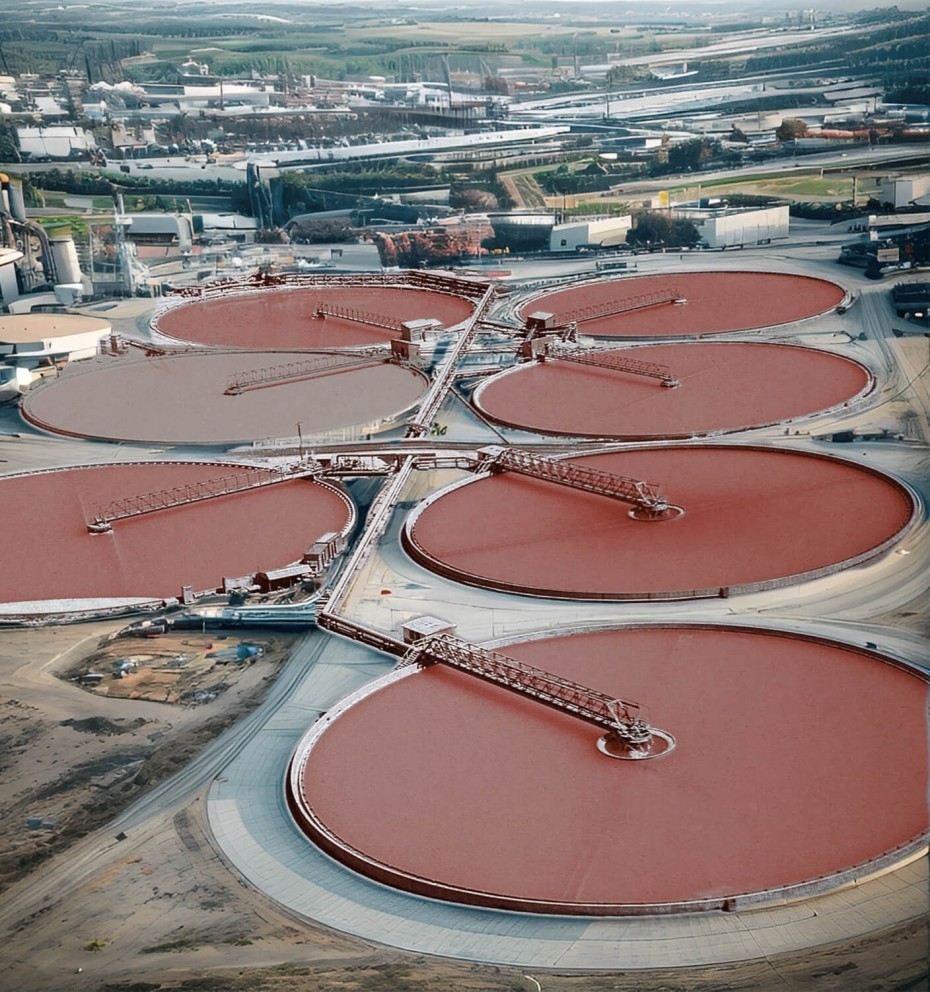

What is Solid Liquid Separation?
Solid-Liquid Separation (SLS) is a critical process, involving the separation of two phases, solid and liquid, from a suspension, which can be essential in numerous sectors such as pulp and paper, wastewater treatment, food and beverage production, chemical manufacturing, mineral beneficiation, and pharmaceuticals for recovery of valuable solid component (the liquid being discarded), for liquid recovery (the solids being discarded), for recovery of both solid and liquid or recovery of neither phase (e.g., when a liquid is being cleaned prior to discharge, as in the prevention of water pollution).
Solid-liquid separation is crucial in enhancing industrial efficiency and sustainability by improving resource recovery, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact. It enables the effective extraction of valuable materials from liquids, reduces energy consumption, and ensures cleaner processes by removing unwanted solids. This leads to reduced disposal costs, lower contamination, and a more sustainable use of water and raw materials in industries such as mineral beneficiation, wastewater treatment, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
Application Industries
_1.png)

_1.png)
_2.png)
-
Metallurgical Industry
(Iron & Steel, Alumina, Copper, Coal Washeries & others) -
Fine Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals
-
Sand & Clay
-
Pulp & Paper
-
Sugar & other Food Industries
-
Cement
-
Industrial Waste & Water Treatment
Methods and Techniques in Solid Liquid Separation
Classification:
Classification is the mechanical operation that aims to separate the solid constituent of a flowing pulp stream into two portions with the help of different settling rates of the solids
Rake Classifier:
A rake classifier is a solid-liquid separation device that operates on the principle of gravity settling, allowing particles to settle based on size and density. The settled solids are conveyed toward the discharge point by a moving mechanism, while the clarified liquid is removed from the top.
Advantages:
- Simple, cost-effective, and reliable
- Suitable for continuous operations
Detritor:
Primarily used in the mining industry, a detritor separates fine, gritty particles from slurries. It operates by generating a vortex within a tank using a rotating drum or rotor, which facilitates particle separation based on size and density.
Advantages:
- Highly efficient for fine particle separation
- Effectively removes abrasive materials from slurries
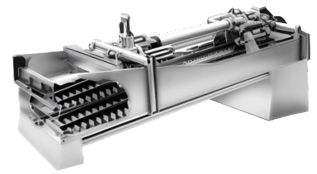
Continuous Vacuum Filtration:
This process is commonly used in industrial applications for the purification or concentration of various substances. The continuous nature of the process makes it highly effective for industries requiring ongoing, high-volume filtration.
Advantages:
- Consistency in filtrate quality
- High-capacity continuous operation
- Automated Operation
Types of Continuous Vacuum Filtration:
- Rotary Vacuum Drum Filter
- Rotary Disc Filter
- Horizontal filter

Sedimentation:
The process by which particles settle out of a fluid such as water or solvent by gravity and accumulate on a surface over time.
Types of Sedimentation:
Gravitational sedimentation: Occurs when particles settle under the influence of gravity.
Flocculation: A process where small particles clump together (flocs) to form larger particles that settle more easily.
Thickener or Clarifier:
Thickeners help increase the density of the solids in a slurry by allowing the finer particles to settle and concentrate at the bottom. It also aids in clarifying the liquid portion by allowing it to rise to the surface.
Sometimes, flocculants (chemical agents) are added to the slurry before thickening. These chemicals help smaller particles clump together into larger flocs, which settle more quickly and efficiently.

Scrubbing
Scrubbing refers to the use of specialized equipment and processes to clean and remove contaminants from industrial environments, surfaces, or gases. The working principle involves Absorption or Adsorption and separation. This process helps maintain safety, efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Types of Srubbers:
- Venturi Scrubber
- Cyclonic Scrubber
- Spray Tower
.png)
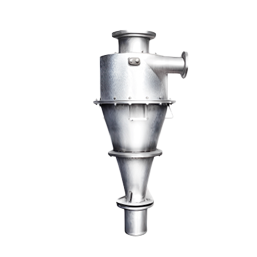
HydroCyclone Separation
It is a technique used primarily in the field of mineral processing, water treatment, and other industries to separate particles in a liquid mixture based on their size and density. It works on the principle of centrifugal force. The denser particles are discharged from the bottom and lighter particles exit from the top.
Advantages:
- Efficiency
- Compact Size
- Cost-Effective
Batch Pressure Filtration
Pressure is applied to a slurry containing solid particles and liquid, which then forces the liquid through a filter medium, leaving the solids behind. It follows a four-step method of slurry loading, filtration, cake formation and discharge.
Advantages:
- High Pressure Efficiency
- Quality discharge
- Robust operation

Benefits of Solid Liquid Separation in Industrial Processes
Efficiency Improvement through Solid-Liquid Separation (SLS):
SLS boosts industrial efficiency by optimizing processes, reducing costs, and improving product quality. Here’s how:
Optimizing Resource Use
- Maximizing Recovery: SLS recovers valuable solids (like metals or by-products) which can be reused, reducing the need for fresh raw materials.
- Water Recycling: SLS enables water recycling in industries like textiles, paper or food processing, lowering water procurement costs.
Enhancing Product Quality
- Preventing Contaminants: SLS removes solid impurities from liquid stream before further processing, maintaining product quality.
- Improved Filtration: In brewing or beverage production, SLS clarifies liquids, ensuring end product is free from unwanted solids and of higher-quality.
Automation and Process Control
- Real-Time Adjustment: Automated systems monitor and optimize parameters for better separation efficiency and productivity.
- Minimizing Errors: Automation reduces manual intervention, ensuring consistent and efficient operations.

Environmental Impact of Solid-Liquid Separation (SLS):
SLS reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste, enhancing resource recovery, reducing pollution, and conserving water and energy. Here's how SLS contributes to sustainability:
Reducing Waste Generation
- Separation of solids allows its diversion to more sustainable disposal promoting recycling. This process also ensures a reduction in waste sent to landfills or incinerators. Valuable materials like metals, by-products, or biological compounds can be recovered and reused, supporting a circular economy.
Water Conservation
- Water can be treated and recycled by solid separation, reducing the need for fresh water and the pressure on local water supplies.
Reducing Pollution
- SLS removes contaminants from wastewater and flue gases, improving water and air quality and helping industries meet environmental regulations.
Preventing Soil and Water Contamination
- SLS captures harmful substances like heavy metals in liquid waste, preventing soil and groundwater pollution.
Mitigating Carbon Footprint
- By improving waste treatment efficiency, SLS lowers greenhouse gas emissions and reduces the energy needed for waste management, helping industries cut their carbon footprint and adopt more sustainable practices.
Enhancing Circular Economy
- SLS supports resource recovery, allowing industries to reuse or recycle materials, such as agricultural waste or precious metals, reducing reliance on virgin resources.

Cost Effectiveness:
Solid Liquid Separtion reduces costs in various industries (wastewater treatment, food processing, etc.) in the following ways:
Waste Handling Costs:
- Efficient solid waste management reduces disposal costs and may generate revenue through recycling.
Recycling and Reuse of Liquids:
- Reusing separated liquids cuts raw material costs and can provide valuable by-products for reuse or sale.
Improved Product Quality:
- SLS helps achieve higher quality final products free from contaminants which can in turn command better market prices and reduce reprocessing costs.
Energy Savings:
- Energy-efficient methods like sedimentation or optimized filtration reduce energy consumption compared to thermal or chemical treatments.
Compliance and Regulatory Savings:
- SLS helps meet environmental regulations, avoiding legal penalties and fines and reducing long-term compliance costs.




